There are many causes of skin pigmentation, including genetics, sun exposure, and even acne. This can make it hard to figure out what’s going on with your skin. The good news is that once you know what’s causing your pigmentation, you can treat it more effectively.
What is pigmentation of the skin?

Before we can help you understand what causes pigmentation of the skin, we should learn a few of the basics about our skin. Skin pigmentation is the natural color of our skin, but it also applies to your hair and eyes. The amount of melanin you produce is what determines your skin tone. The skin is a complicated organ, and various skin disorders can come up with age or exposure to sun exposure or injury. Pigmentation can occur on multiple body parts, including your face, neck, arms, and hands — but it’s most commonly seen on the front. It may look like freckles or age spots, but it can also be caused by hormonal changes or medications (such as birth control pills).
Genetics is a significant factor in determining skin pigmentation.

Genetics is a huge factor in determining skin pigmentation. It’s often the most deciding factor when it comes to your skin color. Our skin color is determined by evolution from thousands of years ago.
Skin pigmentation is related to two types of melanin which are eumelanin and pheomelanin, which have 2 different benefits
- Pheomelanin produces yellow-or orange-toned skin. White skin produces more vitamin D when there is no sun.
- Eumelanin produces dark brown or black tones. Dark skin protects better against UV rays.
What causes pigmentation of the skin?
- Genetics: Your genes determine your skin tone and will affect how your skin pigmentation develops. If you have fair skin, it’s more likely that you’ll develop less pronounced spots of pigmentation than someone with darker skin.
- Age: It’s common for the color of our skin to change with age, especially after those golden years when we start to lose our youthful glow. As we age, the elasticity of our upper layers changes, as does the amount of melanin produced by our melanocytes (cells responsible for producing pigment). This can lead to changes in how dark or light your complexion is overall.
- Ultraviolet (UV) rays: UV radiation from sunlight can cause sunburns and increase your risk of skin cancer. If left untreated, UV rays can also cause discolored patches on your face or body. You must wear sunscreen daily, even during the winter when there aren’t as many hours of sunlight available throughout the day!
- Medications: Certain medications may cause hyperpigmentation because they can increase melanin production within cells over time.Skin conditions: Conditions such as acne vulgaris (aka zits), rosacea (a reddish rash), melasma (darkened areas on the face), and vitiligo (spots caused by loss of pigment) commonly cause discoloration on various parts of the body.
What is skin pigment discoloration?
Skin pigment discoloration is a condition in which the color of your skin changes, making it look lighter or darker than usual.As people age, it’s common to experience some skin pigmentation discoloration. It can happen due to an injury or too much exposure to the sun or wind.
Here we explain the most common types of pigmentation of the skin
- hyperpigmentation
- hypopigmentation
- depigmentation
Hyperpigmentation (dark spots)
 Hyperpigmentation is when you produce too much melanin, which results in dark spots.
Hyperpigmentation is when you produce too much melanin, which results in dark spots.
The leading causes of hyperpigmentation are:
- Sun damage Sun exposure is the primary cause of hyperpigmentation, mainly when young. UV rays can activate melanin, which leads to uneven pigmentation.
- Inflammation. This includes acne breakouts and other skin infections, which can leave behind dark spots after they heal (the same way a bruise does).
- Chemical peels and laser treatments involving light may also lead to excess pigmentation as an unintended side effect if not performed correctly by a licensed professional in these areas. Even slight irritation caused by these processes could result in darker patches appearing on their skin once it heals properly.
- Some types of medication, like birth control pills or antibiotics,
- Pregnancy can cause melasma, or dark spots, to appear on the face.
Hypopigmentation (light spots)
 Hypopigmentation is the opposite of hyperpigmentation. It is a loss of color in the skin due to melanin production being decreased.
Hypopigmentation is the opposite of hyperpigmentation. It is a loss of color in the skin due to melanin production being decreased.
Hypopigmentation is the white spots you see after burns, trauma, inflammatory conditions like psoriasis, eczema, or a genetic disorder. This condition affects people with darker skin tones more than those with lighter tones.
Depigmentation (smooth white patch)

Depigmentation is the loss of skin color and complete loss of pigmentation due to no melanin production.
Skin conditions such as vitiligo, where patches of white appear on your skin due to no melanin production. Or albinism, a rare genetic disorder in which all types of pigments are missing from your body, including melanin and neurotransmitters like dopamine. Aging can also cause depigmentation since there’s less energy available for regenerating new pigment-making cells with age.
Are skin pigmentation problems treatable?
Treatments for pigmentation of the skin disorder will usually depend on what caused it. You may be able to achieve some pigmentation with over-the-counter creams.
However, some conditions may need a prescription from a dermatologist. Avoiding getting sunburned at all costs is the best prevention.
Suppose you have a severe skin pigmentation disorder that doesn’t respond to treatment with over-the-counter products or prescription medications.
In that case, your doctor may suggest laser therapy or other surgical procedures. While these options are typically reserved for more severe cases, they can potentially provide a more permanent solution if you’re willing and able to pay for them.
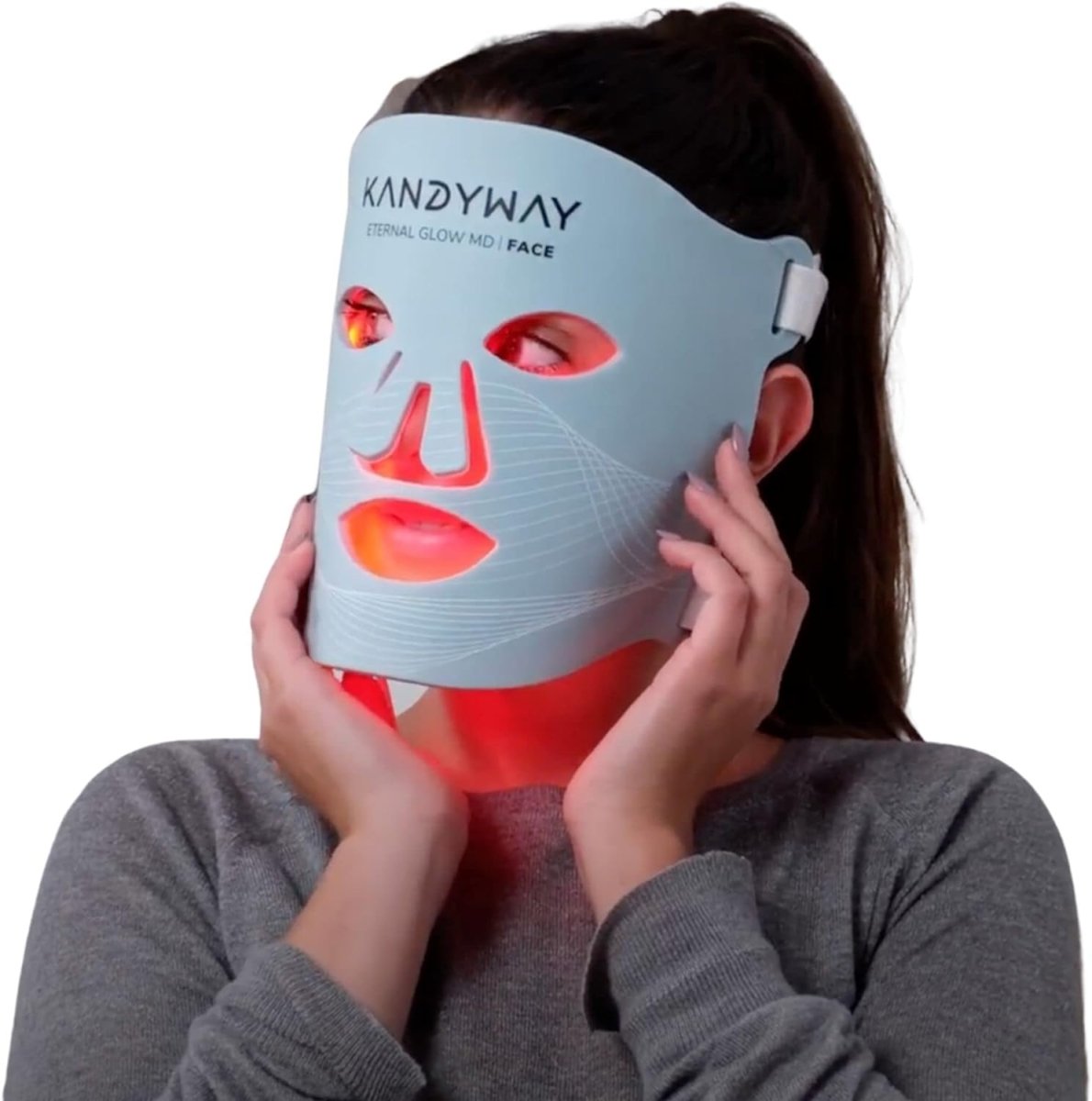
There is some good news, though. Our light therapy mask has been proven to reduce the appearance of pigmentation and wrinkles in 40 + clinical trials.
So you can do everything from the comfort of your home without spending money on pricey treatments at the doctor’s office.
 We recommend only using our medically approved red light therapy mask like the Kandway Eternal Glow. Medically approved means health regulators have verified its efficacy and safety. You only need to use it 3 times a week for 10 minutes each time, and you will notice a massive improvement in your skin after 1 month.
We recommend only using our medically approved red light therapy mask like the Kandway Eternal Glow. Medically approved means health regulators have verified its efficacy and safety. You only need to use it 3 times a week for 10 minutes each time, and you will notice a massive improvement in your skin after 1 month.
Knowing the causes of pigmentation can help you treat it.
Knowing the causes of pigmentation can help you treat it. However, pigmentation is different for everyone, and there are many ways to get it. Sometimes, genetics are responsible for a person’s skin coloration (pigment).
Be honest about what you have exposed your skin to in the past. This will help your dermatologist prescribe the proper treatment solution to you.
Conclusion
Pigmentation of the skin is a normal part of life, but sometimes it can be more than just an annoyance. A dermatologist will determine what kind of pigmentation is present. If you have mild to moderate skin pigmentation disorders, we recommend trying out our Kandway Eternal Glow. It comes with a risk-free trial and will do wonders for lightening pigmentation. www.kandymask.com